Short circuit current is calculated according to IEC 60909 Standard. However, in the standard there will be some statements related to short circuit current, such as prospective short circuit current, initial symmetrical short circuit current, peak short circuit current, breaking current, steady state current, dc component of the short circuit current. It could be more correct to say which current we mention.
Short circuit currents can be calculated on the faulted bus. IEC 60909 includes equations to calculate impedance of power system components, and short circuit analysis is carried out by impedance and currents.
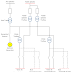
Below is the straightforward example to calculate short circuit current. A generator is connected to transformer and there are faults on 10 kV and 0.38 kV buses. We will find the impedance of the generator and transformer in case of short circuited, and then using the impedances, initial symmetrical short circuit currents based on bus voltage level can be calculated. After the initial symmetrical short circuit currents, peak current, breaking current, steady state current and dc components will be obvious.
Given data for the equipments can be calculated from vendor, equipment datasheet or manufacturer. IEC 60909-2 gives some sample values for the components' impedance in complex number form.
F1 Fault 10 kV
Generator reactance equation comes from IEC 60909.
Reactance equals to subtransient reactance
\[X_d^{''} = \frac{{x_d^{''}}}{{100\% }}.\frac{{{U_{rG}}^2}}{{{S_{rG}}}}\]
\[X_d^{''} = \frac{{0,16}}{{100\% }}.\frac{{{{10}^2}}}{{48}} = 0,3333\Omega\]
If the condition is;
\[{S_{rG}} < 100MVA\]
( rated apperent power of generator)
\[{U_{rG}} > 1kV\]
( rated voltage of generator)
then, fictitious resistance value will be obtained.
\[{R_{Gf}} = 0,07.X_d^{''}\]
\[{R_{Gf}} = 0,07.0,3333 = 0,02333\Omega\]
Correction factor for generator has to be calculated.
\[{K_G} = \frac{{{U_n}}}{{{U_{rG}}}}.\frac{{{c_{\max }}}}{{1 + x_d^{''}.\sqrt {1 - {{\cos }^2}{\varphi _{rG}}} }}\]
\[{K_G} = \frac{{10}}{{10}}.\frac{{1,1}}{{1 + 0,16.\sqrt {1 - 0,{9^2}} }} = 1,02828\]
Armature Resistance of Generator:
\[{R_{Gf}} = {R_a}\]
Fictitious resistance equals to armature resistance
\[\frac{{X_d^{''}}}{{{R_a}}} = \frac{{0,3333}}{{0,0233}} = 14,2587\]
Generator impedance is written down in complex number.
\[{\underline Z _G} = 0,0233 + j0,3333\Omega\]
Corrected generator impedance can be calculated with correction factor.
\[{\underline Z _{GK}} = {K_G}({R_a} + j{X_d}'')\]
\[{\underline Z _{GK}} = 1,02828(0,0233 + jX0,3333)\Omega\]
Impedance at F1 fault location 10 kV bus
\[{\underline Z _{GK}} = {\underline Z _{kF1}} = 0,023993 + j0,342762\Omega\]
Initial symmetrical short circuit current for F1 fault 10 kV (Un) bus
Since faulted bus is 10 kV, impedance at 10 kV of components is used.
\[I_k^{''} = \frac{{c{U_n}}}{{\sqrt 3 {Z_k}}} = \frac{{c{U_n}}}{{\sqrt 3 \sqrt {{R_k}^2 + {X_k}^2} }}\]
\[I_{kF1}^{''} = \frac{{1,1.10}}{{\sqrt 3 .\sqrt {0,{{023993}^2} + 0,{{342762}^2}} }} = 18,4832kA\]
For angle, conjugate math operations,
\[I_{kF1}^{''} = \frac{{1,1.10}}{{\sqrt 3 .(0,023993 + j0,342762)}} = \frac{{6,350853.(0,023993 - j0,342762)}}{{(0,{{023993}^2} + 0,{{342762}^2})}}\]
\[I_{kF1}^{''} = 53,79288.(0,023993 - j0,342762) = 1,290669 - j18,43813kA\]
\[\theta = \arctan \left( {\frac{{ - 18,43813}}{{1,290669}}} \right) = - 85,9958^\circ\]
Peak short circuit current for F1 fault 10 kV bus
\[\kappa = 1,02 + 0,98{e^{ - 3R/X}}\]
\[{i_p} = \kappa \sqrt 2 {I_k}''\]
The equations are from IEC 60909. R/X value is needed for peak current.
\[\frac{{{R_{kF1}}}}{{{X_{kF1}}}} = \frac{{0,023993}}{{0,342762}} = 0,07\]
(Already found from fictitious resistance equation)
\[\kappa = 1,02 + 0,98.{e^{ - 3.(0,07)}} = 1,8143\]
\[{i_p} = 1,8143.\sqrt 2 .18,483 = 47,426kA\]
Breaking Current for F1 fault 10 kV bus
\[{I_b} = \mu .I_{k\max }^{''}\]
Time value is choosen. If the time value is choosen as 0,1 s,
\[t = 0,10s\]
\[\mu = 0,62 + 0,72{e^{ - 0,32I_{kG}^{''}/{I_{rG}}}}\]
However, currents related to generator is needed.
Rated generator current can be calculated easily from traditional power formula.
\[{I_{rG}} = \frac{{{S_{rG}}}}{{\sqrt 3 .{U_{rG}}}}\]
\[{I_{rG}} = \frac{{48}}{{\sqrt 3 .10}} = 2,77128kA\]
Initial symmetrical current on 10 kV will be rated generator current. As there is no other elements contribution to fault current on the 10 kV bus.
\[I_{kF1}^{''} = I_{kG}^{''} = 18,483kA\]
\[\frac{{I_{kG}^{''}}}{{{I_{rG}}}} = \frac{{18,483}}{{2,7712}} = 6,6695\]
\[\mu = 0,62 + 0,72{e^{ - 0,32.6,6695}} = 0,70519\]
Breaking current for breaker is now clear.
\[{I_b}_{F1} = 0,70519.18,483 = 13,0343kA\]
Steady State Current (Ik) for F1 Fault
\[{I_{k\max }} = {\lambda _{\max }}.{I_{rG}}\]
IEC 60909-1 can be used for equation based calculation.
\[\lambda = \lambda \max = \frac{{{u_{f\max }}.\sqrt {1 + 2.{x_{dsat}}.\sin {\varphi _{rG}} + x_{dsat}^2} }}{{{x_{dsat}} - x_d^{''} + (1 + x_d^{''}.\sin {\varphi _{rG}}).{I_{rG}}/I_{kG}^{''}}}\]
\[\sin {\varphi _{rG}} = 0,4358\]
\[\lambda \max = \frac{{1,3.\sqrt {1 + 2.1,5.0,4358 + 1,{5^2}} }}{{1,5 - 0,16 + (1 + 0,16.0,4358).2,7712/18,483}} = 1,8496\]
\[{I_{kF1}} = 1,8496.2,7712 = 5,1259kA\]
DC Component of the short circuit current for F1 Fault
Frequency ( 50 Hz), time 0.1 sn and R/X is now given data.
\[{i_{DC}} = \sqrt 2 .I_k^{''}.{e^{ - 2\pi .f.t.R/X}}\]
\[{i_{DC}} = \sqrt 2 .18,483.{e^{ - 2\pi .50.0,1.0,07}} = 2,898kA\]
Asymmetrical Breaking Current for F1 Fault
It is easy to calculate with dc and breaking current putting into IEC formula.
\[{I_{basyn}} = \sqrt {I_b^2 + i_{DC}^2}\]
\[{I_{basyn}} = \sqrt {13,{{0343}^2} + 2,{{898}^2}} = 13,352kA\]
F2 Fault (0.38 kV)
Transformer Impedance based on 0.4 kV ( Note: Bus voltage is 0,38 kV)
\[{Z_T} = \frac{{{u_{kr}}}}{{100\% }}.\frac{{{U_{rT}}^2}}{{{S_{rT}}}}\]
\[{Z_T} = \frac{{0,0715}}{{100\% }}.\frac{{0,{4^2}}}{5} = 0,002288\Omega\]
Transformer Resistance based on 0.4 kV
\[{R_T} = \frac{{{P_{krT}}}}{{\frac{{{S_{rT}}^2}}{{{U_{rT}}^2}}}}\]
\[{R_T} = \frac{{0,04175}}{{\frac{{{5^2}}}{{0,{4^2}}}}} = 0,0002672\Omega\]
Relative resistive component of the relative impedance
\[{u_{Rr}}\%\]
Z% or
\[{{u_{kr}}}\%\]
\[{u_{Rr}} = \frac{{{P_{krT}}}}{{{S_{rT}}}}.100\%\]
\[{u_{Rr}} = \frac{{0,04175}}{5} = 0,00835 = 0,835\%\]
Transformer reactance
\[{X_T} = \sqrt {{Z_T}^2 - {R_T}^2}\]
\[{X_T} = \sqrt {0,{{002288}^2} - 0,{{0002672}^2}} = 0,002272344\Omega\]
Relative reactance component of the relative impedance
Z% or
\[{{u_{kr}}}\%\]
\[{x_T} = \frac{{{X_T}}}{{\left( {\frac{{U_{rT}^2}}{{{S_{rT}}}}} \right)}}\]
\[{x_T} = \frac{{0,002272344}}{{\left( {\frac{{0,{4^2}}}{5}} \right)}} = 0,0710\]
Transformer Correction Factor
\[{K_T} = 0,95.\frac{{{c_{\max }}}}{{1 + 0,6{x_T}}}\]
\[ c = 1,05\]for low voltage level
\[{K_T} = 0,95.\frac{{1,05}}{{1 + 0,6.0,0710}} = 0,9567\]
\[{\underline Z _{TK}} = {K_T}({R_T} + j{X_T})\]
\[{\underline Z _{TK}} = 0,9567(0,0002672 + j0,002272344)\]
\[{\underline Z _{TK}} = 0,000256 + j0,002174\Omega\]
For F2 Fault, fault at F1 location \[{Z_{kF1}}\] is transferred to 0.38 kV by using transformer turn ratio square
\[{\textstyle{1 \over {t_r^2}}}\]
\[t_r^2 = \frac{{{{10}^2}}}{{0,{4^2}}} = {25^2}\]
\[{\underline Z _{kF1@0,38kV}} = \left( {0,023993 + j0,342762} \right).\frac{1}{{{{25}^2}}} = 3,{83.10^{ - 5}} + j0,00055\Omega\]
Total impedance at F2 fault location
\[{\underline Z _{kF2}} = {\underline Z _{TK}} + {\underline Z _{kF1@0,38kV}} = 0,0002940 + j0,00272\Omega\]
Initial symmetrical short circuit current for F2 0,38 kV
\[I_k^{''} = \frac{{c{U_n}}}{{\sqrt 3 {Z_k}}}\]
\[I_{kF2}^{''} = \frac{{1,05.0,38}}{{\sqrt 3 .\sqrt {0,{{0002940}^2} + 0,{{00272}^2}} }} = 84,1266kA\]
Peak short circuit current for F2 fault 0,38 kV bus
\[\frac{{{R_{kF2}}}}{{{X_{kF2}}}} = \frac{{0,0002940}}{{0,00272\Omega }} = 0,1080\]
\[\kappa = 1,02 + 0,98{e^{ - 3.0,1080}} = 1,728\]
\[{i_p}_{F2} = 1,728.\sqrt 2 .82,1266 = 205,678kA\]
Breaking Current for F2 fault
\[{I_b}_{F2} = I_{kF2}^{''} = 84,1266kA\]
Steady State Current (Ik) for F2 Fault
\[{I_k}_{F2} = I_{kF2}^{''} = 84,1266kA\]
DC Component of the short circuit current for F2 Fault
\[{i_{DC}} = \sqrt 2 .84,1266.{e^{ - 2\pi .50.0,1.0,1080}} = 3,998kA\]
Asymmetrical Breaking Current for F2 Fault
\[{I_{basyn}} = 84,2216kA\]









0 Yorumlar